Pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS) typically presents with dull, aching pelvic pain or a sensation of heaviness, which is often worsened by prolonged standing, walking, or following intercourse. The symptoms result from incompetent ovarian veins, leading to blood pooling within the pelvis.
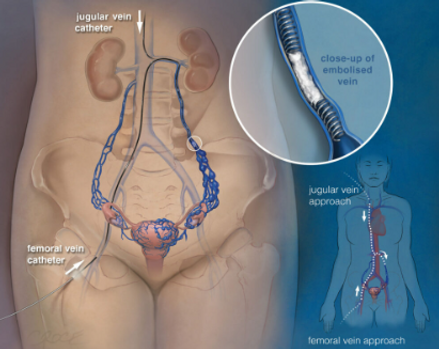
The treatment involves embolization, a minimally invasive outpatient procedure performed under local anesthesia. A small puncture is made on the right side of the neck, through which a catheter is inserted. The ovarian veins are then embolized using a combination of coils and sclerosant agents to block abnormal blood flow. During the procedure, the pelvic veins are also examined, and if abnormalities are identified, they are embolized as well.
Most patients experience significant relief from their symptoms within the first 24 to 48 hours following the procedure

Pre and post embolization images of the first ever pelvic congestion syndrome embolization carried out at the Lismore Base Hospital in Australia carried out by Dr Naushad Karim. The procedure was carried out as a daycase and the patient reported immediate relief of symptoms
Frequently Asked Questions

What are the symptoms of pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS)?
Pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS) causes chronic pelvic pain due to enlarged veins in the pelvic region, particularly around the ovaries. Symptoms include:
-
Pelvic pain: A dull ache, heaviness, or throbbing that may worsen with prolonged standing, sitting, or during/after intercourse.
-
Varicose veins: Not only in the legs but also in the vulva, buttocks, or thighs.
-
Urinary symptoms: Increased urinary frequency, urgency, or pain.
-
Gastrointestinal symptoms: Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)-like symptoms, including bloating, constipation, or diarrhea.
What causes pelvic congestion syndrome?
PCS occurs due to venous insufficiency, where veins in the pelvis (particularly the ovarian veins) become enlarged or dilated. This results in blood pooling and backflow (reflux), causing pain and discomfort.
Do I need a referral from a gynecologist?
Yes, it is advisable to consult with a gynecologist first. They will conduct an evaluation and rule out other potential causes for your symptoms. If you don’t have a gynecologist, we can help arrange an appointment.
What should I bring to the consultation?
Please bring:
-
All your previous medical reports and scans.
-
A referral note from your gynecologist, if available.
What should I expect on the day of the procedure?
-
Fasting: Please come fasting for the procedure.
-
After check-in, an IV line will be placed, and our team will explain the procedure and obtain your consent.
-
You'll be taken to the procedure room afterward.
How is the procedure carried out?
The procedure is minimally invasive and performed under local anesthesia (you will be awake). Here's what to expect:
-
A needle is inserted into a vein on the right side of your neck.
-
A catheter and wire are used to access the ovarian veins.
-
The veins are treated with coils (small metal particles) and sclerosant (a chemical to seal abnormal veins).
-
Additional pelvic veins may also be embolized if necessary.
-
During the procedure, you may be asked to hold your breath or bear down. Afterward, a small bandage will be applied to your neck, and you can return home in about 30 minutes.
How long will it take for my symptoms to improve?
Most patients experience significant symptom improvement within one week following the procedure.
Who do I follow up with after the procedure?
We recommend a follow-up consultation one week after the procedure to check on your recovery and assess symptom resolution.